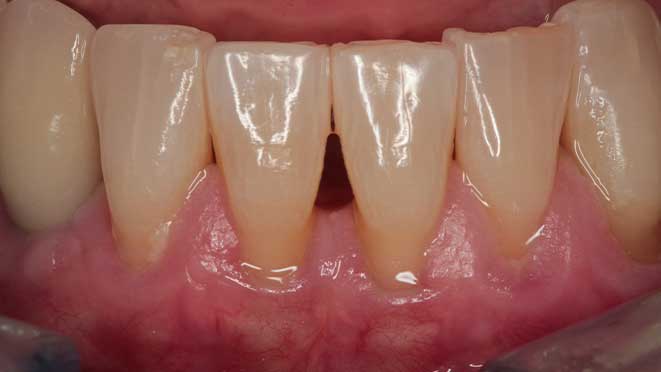
Understanding Osseous Surgery
Why Is Osseous Surgery Needed?
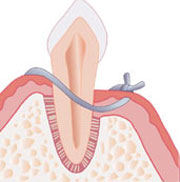
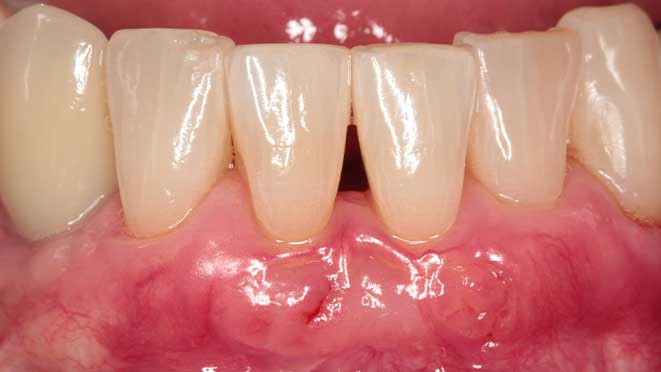
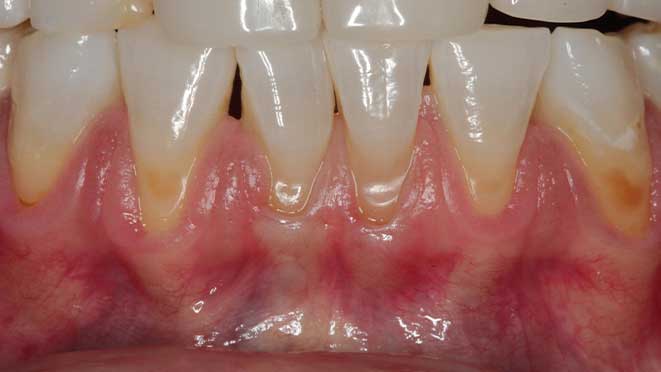
Osseous surgery becomes necessary when a patient experiences severe gum disease or periodontitis. In periodontitis, pockets form between the teeth and the gum tissue, leading to the loss of supporting bone structure. The purpose of osseous surgery is to remove bacteria and damaged tissues from these pockets, preserve the healthy tissue, and help regrow the bone where possible. In severe cases of gum disease, osseous surgery may be the only way to restore the gumline to prevent tooth loss, further bone loss, and other dental complications.
Types of Osseous Surgery
Several types of osseous surgeries may be performed. The most common type is flap surgery, where the dentist lifts a part of your gum tissue to access the underlying root and bone structure. Once there, they can remove the bacteria and damaged tissues before suturing the gum back to its original position. Another type of osseous surgery is bone grafting where the dentist replaces the lost bone with a grafting material made from your bone or synthetic material.
Who Needs Osseous Surgery?
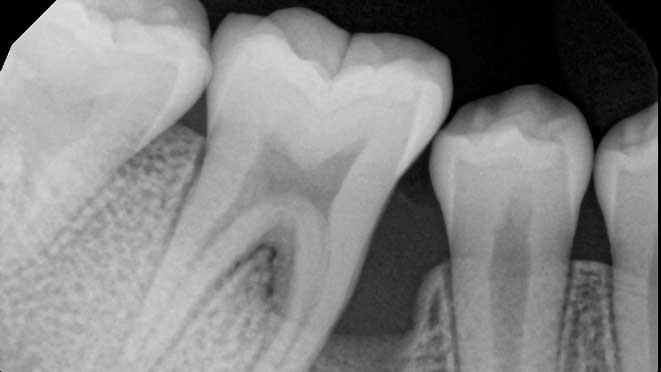
If you have severe gum disease or periodontitis, your dentist may recommend osseous surgery. Signs that may indicate a patient is a candidate for osseous surgery include, deep pockets in the gums, gum recession, mobility of teeth, bone loss, swelling or inflammation of the gums, and pus coming out of between your teeth and gums. Your dentist will thoroughly analyze your dental history, X-rays, and other diagnostic data to determine whether or not osseous surgery is necessary.
The Process of Osseous Surgery:
Pre-Operation:
Before osseous surgery, the dentist will carry out some diagnostic imaging and consult with you to understand your medical history thoroughly. During the consultation, they will explain the procedure, answer any questions you may have, and give you instructions about diet modification and self-care before the surgery.
Operation:
On the day of surgery, your dentist will use local anesthesia to numb the treatment area. Next, they will carefully remove the bacteria and damaged tissues from the pockets, clean the tooth root, and smooth the bone surface to help with healing. After this, the dentist will trim away any excess gum tissue that is contributing to your gum disease before stitching the gum tissue back into position. Finally, you will be given pain medication and instructions on how to care for your gums properly during the postoperative period.
Post-Operation:
After your surgery, you will come in for a follow-up appointment to remove your stitches and ensure that your healing process is going well. Your dentist will advise you on self-care instructions like proper brushing and flossing techniques, diet modifications, and when you can resume regular activities.
Recovery After Osseous Surgery:
Preparing for Recovery:
Before your procedure, it's important to prepare for your recovery by arranging time off from work, organizing your medications and taking care of chores that may become difficult after the surgery. We recommend that patients follow a diet of soft foods for at least two weeks until the stitches have healed.
Managing Pain and Other Post-Operation Symptoms:
It's normal to experience some pain, swelling, or discomfort after osseous surgery. Patients can take over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen to manage pain. While recovering, it's essential to avoid smoking, using straws, or spitting as they can dislodge the blood clots and hinder proper healing.
What to Expect During Recovery:
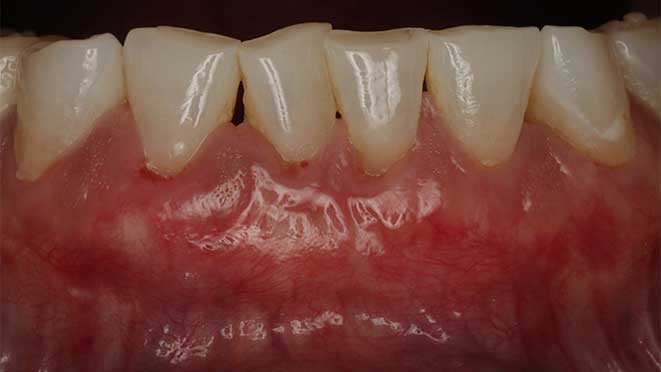
Typically, after osseous surgery, patients experience mild discomfort for the first few days. However, the amount of discomfort will vary depending on the extent of the surgery. It's normal to notice some bleeding or discomfort when you brush or floss for the first few days. You may also experience swelling or inflammation during the first week. Gently rinsing your mouth with warm saltwater can help alleviate some of these symptoms.
Benefits of Osseous Surgery:
Restoring Normal Oral Functions:
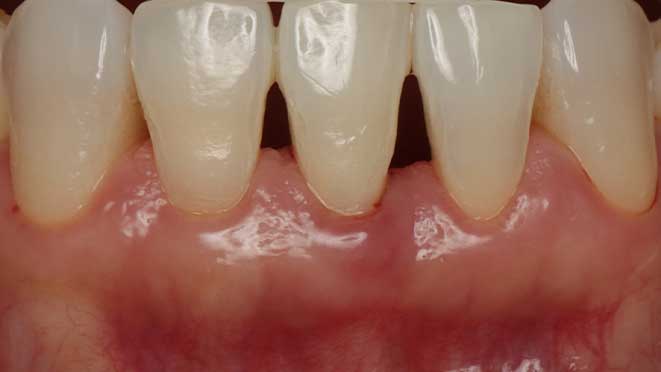
Osseous surgery helps restore the normal function of your teeth, mouth, and jawbone. The surgery helps preserve the support structure around your teeth, preventing further bone loss and eventual tooth loss.
Prevention of Future Dental Problems:
Post-surgery, your gums and teeth can heal fully without the harmful bacteria, promoting your dental hygiene and preventing future dental issues.
Improvement of Oral Health:
Osseous surgery significantly improves your oral health, reducing the likelihood of future dental procedures. This surgery provides a long-term solution to receding gum lines and bone loss, allowing patients to enjoy a healthy, beautiful smile.
Risks and Limitations of Osseous Surgery:
Risks of Osseous Surgery:
Patients may experience risks such as infection, bleeding, pain, sensitivity, allergic reactions, or loosening of your teeth. However, these risks are rare and with proper care and follow-up, complications are minimized.
Limitations of Osseous Surgery:
Osseous surgery may not be an ideal procedure for all patients. Patients with diabetes, heart disease, or other underlying medical conditions may need to take additional precautions before surgery. Your dentist will thoroughly evaluate your case to ensure you achieve the best possible outcome.
When Osseous Surgery is Not Recommended:
Osseous surgery is not recommended for pregnant women, those taking certain medications, or those with active infections. Your dentist will evaluate your overall health before recommending this procedure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, osseous surgery is a procedure that can restore damaged gums and bones around your teeth, promote proper healing, and help prevent future dental issues. Understanding whether you need it, what it entails, and what to expect from recovery is the first step in seeking the best possible dental care for your dental health. With the right aftercare, you can recover adequately and enjoy a healthier, stronger, and more attractive smile. It is essential to discuss the benefits, risks, and limitations of osseous surgery with your dentist to develop a personalized treatment plan that works for you. We encourage you to work with your dentist to promote optimal oral health, so you can enjoy a lifetime of healthy teeth and a beautiful smile.